Mean free path: Assuming the radius of diatomic molecules is approximately 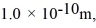 for what pressure will the mean free path in room-temperature (20°C) nitrogen be 4.6 m? The Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K, Avogadro's number is 6.02 × 1023 molecules/mole, and the ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol ∙ K = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/mol ∙ K.
for what pressure will the mean free path in room-temperature (20°C) nitrogen be 4.6 m? The Boltzmann constant is 1.38 × 10-23 J/K, Avogadro's number is 6.02 × 1023 molecules/mole, and the ideal gas constant is R = 8.314 J/mol ∙ K = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/mol ∙ K.
Definitions:
Fertilization
The process by which sperm and egg combine to form a zygote, initiating embryonic development.
Ovum
A female gamete or egg cell that, when fertilized by a sperm, begins the process of developing into a new organism.
Sperm
Male reproductive cells or gametes in sexually reproducing organisms that combine with the female gamete, leading to fertilization and the development of a new organism.
Teratogen
Any factor that can cause a birth defect.
Q1: Inductive ammeters work because of what principle?<br>A)
Q5: First law of thermodynamics: In an isochoric
Q5: Spherical capacitors: Two thin-walled concentric conducting spheres
Q8: Which act or organization regulates air-conditioning refrigerant?<br>A)
Q24: Finite line of charge: Two thin 80.0-cm
Q31: Heat engines: A nuclear fission power plant
Q32: Capacitors in combination: Three capacitors, of capacitance
Q42: Charge in an electric field: A small
Q44: Coulomb's law: In the figure Q =
Q99: Sound: What characteristic of sound determines the