Heat engines: A real (non-Carnot) heat engine, operating between heat reservoirs at temperatures of  and
and 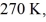 performs 2.4 kJ of net work and rejects
performs 2.4 kJ of net work and rejects  of heat in a single cycle. The thermal efficiency of this heat engine is closest to
of heat in a single cycle. The thermal efficiency of this heat engine is closest to
Definitions:
Nonparametric Techniques
Statistical methods that do not assume a specific distribution for the data they are analyzing.
Parametric Techniques
Statistical methods based on assumptions about the distribution of the underlying population from which the sample data are drawn.
Confidence Interval
A range of values, derived from statistical analysis, that is likely to contain the value of an unknown parameter with a specified level of confidence.
Null Hypothesis
A theory that assumes there is no statistical significance in a set of given observations, with the aim of testing the validity of this assumption.
Q4: Potential energy of point-charges: An electron is
Q6: What are the other names for a
Q12: Meters: A galvanometer G has an internal
Q24: RC circuits: An uncharged 30.0-µF capacitor is
Q38: Motion of a charged particle: A pair
Q50: First law of thermodynamics: A cylinder contains
Q51: Charged ring: A charge Q = -820
Q54: Kirchhoff's rules: For the circuit shown in
Q72: Shock waves: A jet aircraft, in level
Q73: Thermal expansion: The exterior of a supersonic