Suppose that in order to estimate of the average effect of participation in a job training program (train) on wage, you included controls for education (educ) , years of experience (exper) in your model: log(wage) = 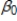 +
+ 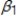
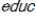 +
+ 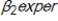 +
+ 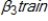 + u . Which of the following is a reason why the coefficient,
+ u . Which of the following is a reason why the coefficient, 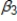 , might be biased?
, might be biased?
Definitions:
Gantt Chart
A visual scheduling tool that outlines project timelines, tasks, and milestones in a horizontal bar chart format.
PERT Network
A project management tool used to schedule, organize, and coordinate tasks within a project, emphasizing the analysis of task sequences and durations.
Measurable Objectives
Specific, quantifiable, achievable goals set to evaluate the success of a project, employee performance, or organizational outcomes.
Effective Project Managers
Individuals who successfully plan, execute, and close projects, meeting or exceeding stakeholders' expectations through skilled leadership and problem-solving.
Q6: The normality assumption implies that:<br>A)the population error
Q7: Which of the following assumptions is required
Q22: Consider the following regression equation: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/.jpg"
Q45: Which term means the irreversible loss of
Q48: Involves assisting clients in purchasing stocks and
Q60: Involves analyzing and making recommendations on the
Q71: To reduce the risk of elder maltreatment,
Q99: Sensitivity to smell declines throughout adulthood beginning
Q111: The transition to retirement begins shortly before
Q150: The rate of mortality for those who