Suppose that in order to estimate of the average effect of participation in a job training program (train) on wage, you included controls for education (educ) , years of experience (exper) in your model: log(wage) = 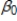 +
+ 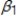
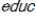 +
+ 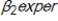 +
+ 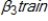 + u . Which of the following is a reason why the coefficient,
+ u . Which of the following is a reason why the coefficient, 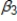 , might be biased?
, might be biased?
Definitions:
Target Payoffs
Expected or desired financial returns from an investment strategy or economic activity.
Collusion
An agreement between firms, typically secret, to limit competition among themselves, such as by setting prices or output levels.
Diagram
A simplified drawing showing the appearance, structure, or workings of something in a conceptual or visual form.
Profits
The financial gain realized when the revenue earned from a business activity exceeds the expenses, costs, and taxes needed to sustain the activity.
Q3: Pooled ordinary least squares estimation is commonly
Q7: Parkinson's symptoms can be treated with _.<br>A)
Q8: If <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8272/.jpg" alt="If <sub>j</sub>,
Q9: When a series has the same average
Q10: The centering of explanatory variables about their
Q16: Which of the following highlights a requirement
Q21: Predictions of a dependent variable are subject
Q22: Which of the following statements is true?<br>A)When
Q31: _ are crucial elements of the financial
Q78: $1,000 invested today at 6% interest would