Fager Clinic uses client-visits as its measure of activity. During February, the clinic budgeted for 2,390 client-visits, but its actual level of activity was 2,440 client-visits. The clinic has provided the following data concerning the formulas used in its budgeting and its actual results for February:Data used in budgeting: 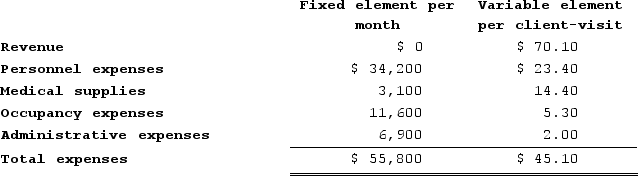 Actual results for February:
Actual results for February: The revenue variance for February would be closest to:
The revenue variance for February would be closest to:
Definitions:
LIFO Inventory
LIFO inventory is a method of inventory valuation where the most recently produced or purchased items are recorded as sold first, potentially reducing taxes in periods of inflation.
Sales Exceed Production
A situation where the demand for a company's products surpasses its current production capacity or available inventory.
Variable Costing
An accounting method that only includes variable costs—costs that vary with production levels—when calculating the cost of producing a good or service.
Net Operating Income
The profit generated from a company’s everyday business operations, calculated by subtracting operating expenses from revenue.
Q19: Hesterman Corporation makes one product and has
Q27: The following information was taken from the
Q67: Which data collection method is the most
Q94: Dilly Farm Supply is located in a
Q128: Davis Corporation is preparing its Manufacturing Overhead
Q191: Sarafiny Corporation is in the process of
Q292: Kawamura Kennel uses tenant-days as its measure
Q337: Wagster Urban Diner is a charity supported
Q415: Rameriz Corporation is a shipping container refurbishment
Q464: Stegemann Corporation is a shipping container refurbishment