Table 5.2
A company makes four products that have the following characteristics: Product A sells for $75 but needs $20 of materials and $20 of labor to produce; Product B sells for $90 but needs $45 of materials and $20 of labor to produce; Product C sells for $110 but needs $50 of materials and $30 of labor to produce; Product D sells for $135 but needs $75 of materials and $40 of labor to produce. The processing requirements for each product on each of the four machines are shown in the table.
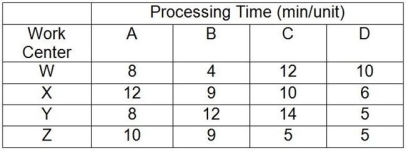
Work centers W, X, Y, and Z are available for 40 hours per week and have no setup time when switching between products. Market demand is 50 As, 60 Bs, 70 Cs, and 80 Ds per week. In the questions that follow, the traditional method refers to maximizing the contribution margin per unit for each product, and the bottleneck method refers to maximizing the contribution margin per minute at the bottleneck for each product.
-Use the information in Table 5.2. Using the bottleneck method, what is the profit if the company manufactures the optimal product mix (consider variable costs only-overhead is not included in this profit calculation) ?
Definitions:
Price Ceiling
A legal maximum price set by the government for goods and services, intended to prevent prices from rising above a certain level.
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a product offered is equal to the quantity of the product in demand, leading to market stability where there is no shortage or surplus.
Temporary Surplus
A situation where the supply of a product exceeds its demand for a short period, often leading to price reductions.
Quantity Supplied
The amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to sell at a particular price.
Q12: What is a capacity cushion? Provide examples
Q13: The theory of constraints accepts existing system
Q19: A wait-and-see capacity strategy minimizes the chances
Q21: Using Table 7.14, which activity has the
Q42: Value stream maps consist of a(n)_, a(n)_,
Q48: Firms that have highly repetitive processes and
Q48: Using Table 7.14, what is the probability
Q82: Which one of the following factors usually
Q89: Forecasts almost always contain errors.
Q182: Historically, the average proportion of defective bars