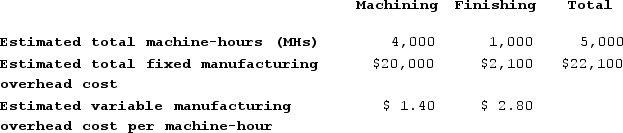
Bierce Corporation has two manufacturing departments--Machining and Finishing. The company used the following data at the beginning of the year to calculate predetermined overhead rates:
 During the most recent month, the company started and completed two jobs--Job B and Job K. There were no beginning inventories. Data concerning those two jobs follow:
During the most recent month, the company started and completed two jobs--Job B and Job K. There were no beginning inventories. Data concerning those two jobs follow:
 Required:a. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate that overhead rate. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)b. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the amount of manufacturing overhead applied to Job B. (Do not round intermediate calculations.)c. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the amount of manufacturing overhead applied to Job K. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.)d. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Machining department? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)e. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Finishing department? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)f. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job B? (Do not round intermediate calculations.)g. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job K? (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
Required:a. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate that overhead rate. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)b. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the amount of manufacturing overhead applied to Job B. (Do not round intermediate calculations.)c. Assume that the company uses a plantwide predetermined manufacturing overhead rate based on machine-hours. Calculate the amount of manufacturing overhead applied to Job K. (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.)d. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Machining department? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)e. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. What is the departmental predetermined overhead rate in the Finishing department? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)f. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job B? (Do not round intermediate calculations.)g. Assume that the company uses departmental predetermined overhead rates with machine-hours as the allocation base in both production departments. How much manufacturing overhead will be applied to Job K? (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
Definitions:
Controlled Adaptation
The deliberate adjustment or modification of behavior or processes in response to changing conditions or environments.
Structural Family Therapist
A therapist trained in identifying and restructuring the organizational hierarchy and subsystems within a family to alleviate dysfunction.
Overly Permeable Boundaries
This term typically refers to a situation where an individual or system has boundaries that are too loose, allowing for unhealthy or unwanted intrusions.
Dysfunctional Mimesis
Involves the problematic imitation or reproduction of behaviors or attitudes that are unhealthy or unproductive, often in a social or interpersonal context.
Q49: Management of Mcgibboney Corporation has asked your
Q89: The management of Garn Corporation would like
Q91: The cost of electricity for running production
Q141: All other things the same, if long-term
Q143: During December, Moulding Corporation incurred $76,000 of
Q147: The amount that a manufacturing company could
Q230: Streif Incorporated a local retailer, has provided
Q299: Henkes Corporation bases its predetermined overhead rate
Q324: The Seabury Corporation has a current ratio
Q392: The management of Schneiter Corporation would like