Segers Corporation manufactures one product. It does not maintain any beginning or ending Work in Process inventories. The company uses a standard cost system in which inventories are recorded at their standard costs and any variances are closed directly to Cost of Goods Sold. There is no variable manufacturing overhead. The company's balance sheet at the beginning of the year was as follows:
 The standard cost card for the company's only product is as follows:
The standard cost card for the company's only product is as follows:
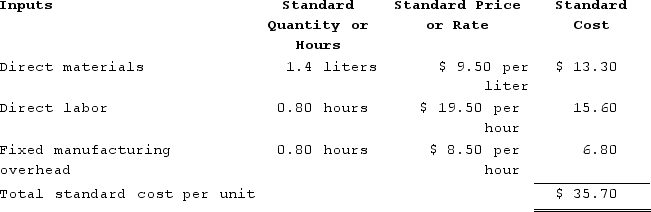 The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $238,000 and budgeted activity of 28,000 hours.
The standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate was based on budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead of $238,000 and budgeted activity of 28,000 hours.
During the year, the company completed the following transactions:a. Purchased 51,000 liters of raw material at a price of $9.20 per liter.b. Used 46,100 liters of the raw material to produce 33,000 units of work in process.c. Assigned direct labor costs to work in process. The direct labor workers (who were paid in cash) worked 26,200 hours at an average cost of $19.90 per hour.d. Applied fixed overhead to the 33,000 units in work in process inventory using the predetermined overhead rate multiplied by the number of direct labor-hours allowed. Actual fixed overhead costs for the year were $251,800. Of this total, $165,800 related to items such as insurance, utilities, and indirect labor salaries that were all paid in cash and $86,000 related to depreciation of manufacturing equipment.e. Transferred 33,000 units from work in process to finished goods.f. Sold for cash 34,800 units to customers at a price of $44.00 per unit.g. Completed and transferred the standard cost associated with the 34,800 units sold from finished goods to cost of goods sold.h. Paid $156,000 of selling and administrative expenses.i. Closed all standard cost variances to cost of goods sold.
Required:1. Compute all direct materials, direct labor, and fixed overhead variances for the year.2. Enter the beginning balances and record the above transactions in the worksheet that appears below.
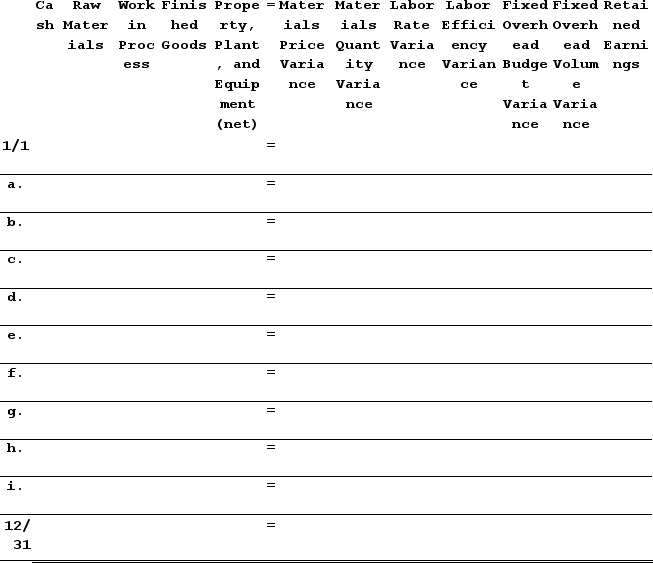 3. Determine the ending balance (e.g., 12/31 balance) in each account.
3. Determine the ending balance (e.g., 12/31 balance) in each account.
Definitions:
Accounts Payable
The amount a company owes to suppliers for goods and services purchased with credit.
Factor
A finance company to which businesses sell their accounts receivable—usually for a percentage of the total face value.
Q3: Which statements should a nurse include when
Q37: Information on Westcott Corporation's direct labor costs
Q46: Wolery Incorporated has provided the following data
Q66: Robins Corporation manufactures one product. It does
Q76: Ken and Jim agree to go into
Q79: Tax considerationsshould always be the primary reason
Q95: Grub Chemical Corporation has developed cost standards
Q169: Phann Corporation manufactures one product. It does
Q208: Mongar Corporation applies manufacturing overhead to products
Q213: Dirickson Incorporated has provided the following data