Suppose you want to use the Wilcoxon rank sum test to detect a shift in distribution 1 to the right of distribution 2, based on samples of sizes 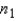 = 7 and
= 7 and  = 9.
= 9.
Should you use T1 or T1* as the test statistic?
______________
What is the rejection region for the test if 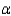 = 0.05?
= 0.05?
Reject 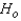 if the test statistic
if the test statistic 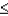 ______________.
______________.
What is the rejection region for the test if 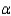 = 0.01?
= 0.01?
Reject 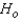 if the test statistic
if the test statistic 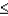 ______________.
______________.
Definitions:
Achievement Motivation
The drive or urge to accomplish goals or attain certain standards of excellence.
Canadian Population
The total number of people living in Canada, encompassing a diverse range of ethnic, cultural, and linguistic groups.
Homosexual
An adjective describing individuals who are romantically or sexually attracted to people of the same sex.
Affiliation Motivation
The drive to relate to people on a social basis and to be accepted into groups.
Q12: Growth in the size of government has
Q25: A(n) _ instrument of public policy collects
Q33: A _ describes a situation in which
Q43: In developing a 90% confidence interval for
Q49: The policy-making stage of _ is where
Q57: Because of greater decentralization of policy making
Q86: In multiple regression, the prediction equation <img
Q110: A multiple regression model has the form
Q144: The Wilcoxon rank sum test is a
Q150: A regression analysis between weight (y in