If we want to relate a random variable y to two-independent variables 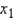 and
and 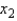 , a regression hyperplane is the three-dimensional equivalent of a regression line that minimizes the sum of the squared vertical deviations between the sample points suspended in y vs.
, a regression hyperplane is the three-dimensional equivalent of a regression line that minimizes the sum of the squared vertical deviations between the sample points suspended in y vs. 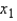 vs.
vs. 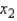 space and their associated multiple regression estimates, all of which lie on this hyperplane.
space and their associated multiple regression estimates, all of which lie on this hyperplane.
Definitions:
Q9: To be valid, the chi-square test requires
Q22: Americans are very vocal about their
Q27: Which one of the following statements correctly
Q29: The ideology of individual members of Congress
Q56: About _ % of states allow citizen-generated
Q98: Apply the Friedman test to the accompany
Q105: The rank correlation coefficient is used when
Q123: The width of the confidence interval estimate
Q139: In the randomized block design ANOVA, the
Q140: The analysis of variance, ANOVA, is best