Suppose a regression analysis based on the model 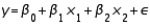 with 15 observations produced SSE = 3.55,
with 15 observations produced SSE = 3.55, 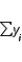 = 13.131, and
= 13.131, and 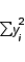 = 125.1. Hence, the proportion of the total variability in y that is accounted for by
= 125.1. Hence, the proportion of the total variability in y that is accounted for by 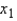 and
and 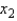 is:
is:
Definitions:
Working Memory
The part of the information-processing system where active thinking takes place, and information from the sensory register may be combined with memory of past experiences.
Long-term Memory
The phase of memory capable of storing an unlimited amount of information indefinitely, ranging from a few minutes ago to as far back as one can remember.
Theory of Mind
The ability to attribute mental states—beliefs, intents, desires, emotions—to oneself and others and to understand that others have beliefs and desires different from one's own.
Beliefs and Desires
The mental attitudes and inclinations that influence a person's motivations and actions.
Q1: Discuss some of the signals for the
Q5: Stepwise regression is a statistical technique that
Q15: In developing a simple linear regression model,
Q15: Which of the following is not true
Q40: Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a procedure
Q49: The area to the right of a
Q54: A direct relationship is a relationship between
Q85: One-way ANOVA is applied to three independent
Q122: The completely randomized design is an experimental
Q151: When testing <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8220/.jpg" alt="When testing