Two independent samples are selected at random from two normal populations. The sample statistics are as follows: 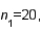
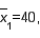
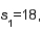
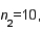
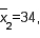 and
and 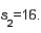 Assume that a two-tailed hypothesis test is conducted at
Assume that a two-tailed hypothesis test is conducted at 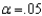 , what is the critical value?
, what is the critical value?
Definitions:
Affect Heuristic
A mental shortcut in decision-making influenced by emotions, where people rely on feelings rather than detailed analysis.
Q16: Suppose a 90% confidence interval for the
Q49: Assuming that all necessary conditions are met,
Q75: In order to predict with 95% confidence
Q98: A recent survey indicates that the proportion
Q119: In a simple linear regression problem, the
Q133: When the necessary conditions are met, a
Q137: A randomized block design with 4 treatments
Q139: If you were constructing a 99% confidence
Q188: Both the equal-variances and unequal variances test
Q210: From a sample of 400 items, 14