Two independent random samples of sizes 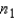 = 4 and
= 4 and 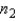 = 5 are selected from each of two normal populations:
= 5 are selected from each of two normal populations: 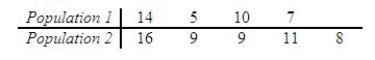 Calculate
Calculate 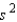 , the pooled estimator of
, the pooled estimator of 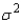 .
.
______________
Find a 90% confidence interval for ( 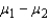 ), the difference between the two population means.
), the difference between the two population means.
CI = ______________ Enter (n1, n2)
Test  for
for 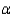 = 0.05.
= 0.05.
Conclusion:
We ______________ have sufficient evidence to indicate 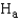 .
.
Definitions:
Species Richness
A measure of the number of different species represented in an ecological community, landscape or region.
Disturbance Hypothesis
posits that disturbances in an ecosystem can create opportunities for new species to colonize, thus affecting biodiversity.
Mycorrhizae
A symbiotic association between a fungus and the roots of a vascular host plant, enhancing nutrient and water absorption.
Fungi
A kingdom of spore-producing organisms that feed on organic matter, including molds, yeast, and mushrooms.
Q35: Suppose you wish to estimate a population
Q46: The daily wages in a particular industry
Q50: We can use either the z-test or
Q100: A 90% confidence interval for the population
Q115: In constructing a confidence interval estimate for
Q153: A confidence interval for the population mean
Q157: Which of the following exemplifies a Type
Q173: The mean of the sampling distribution of
Q198: Based on sample data, the 90% confidence
Q208: Which of the following statements about the