A two-tailed hypothesis test of the population mean is used when the alternative hypothesis takes the form 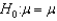 .
.
Definitions:
Comparative Advantage
The ability of a country or firm to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost than its competitors, leading to more efficient trade and production patterns.
Absolute Advantage
A situation in which a country, individual, or company can produce a particular good or service more efficiently than another party, using the same amount of resources.
Trade
Trade involves the exchange of goods, services, or both between parties, which can be at the domestic or international level, fostering economic interaction and integration.
Opportunity Cost
The potential benefits an individual, investor, or business misses out on when choosing one alternative over another.
Q2: In a paired-difference experiment, two samples of
Q8: Which of the following correctly describes a
Q48: Independent samples of n<sub>1</sub> = 400 and
Q116: A paired-difference experiment was conducted using 10
Q139: Using the standard normal curve, the z-score
Q140: Given N = 1,000, n = 30,
Q142: Using the standard normal curve, the z-score
Q151: The test statistic of the single-factor ANOVA
Q151: The margin of error equals the sum
Q199: If we reject the null hypothesis <img