A random sample of n = 36 observations from a quantitative population produced a mean 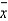 = 2.5 and a standard deviation s = 0.30. Suppose your research objective is to show that the population mean
= 2.5 and a standard deviation s = 0.30. Suppose your research objective is to show that the population mean 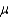 exceeds 2.4.
exceeds 2.4.
Find the standard error of the mean.
______________
Do the data provide sufficient evidence to indicate that 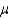 > 2.3. Test at
> 2.3. Test at 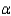 = 0.05.
= 0.05.
Test statistic = ______________
Critical Value(s) = ______________
Conclusion: ______________
Interpretation: __________________________________________
Calculate the p-value for the test statistic above.
p-value = ______________
Use the p-value to draw a conclusion at the 5% significance level.
Conclusion: ______________
Compare the two conclusions. Are they the same?
______________
Find the critical value of 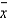 used for rejecting H0.
used for rejecting H0.
______________
Calculate 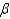 = P(accept H0 when
= P(accept H0 when 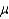 = 2.5).
= 2.5).
______________
Definitions:
Temporal Precedence
The principle that establishes the need for a cause to occur before its effect, crucial in establishing causal relationships in research.
Causation
The action of causing something, indicating a relationship between two events where one directly effects the change in the other.
Behavior
The actions or reactions of an object or organism, often in response to its environment or stimuli.
Alternative Explanations
Other possible interpretations or reasons that could account for observed outcomes or phenomena, challenging the initial hypothesis.
Q4: If x is a normal random variable
Q25: Suppose in testing a hypothesis about a
Q58: A political analyst in Michigan surveys a
Q59: Suppose that the probability p of success
Q85: The test statistic that is used in
Q95: Suppose a 95% confidence interval for the
Q97: For which of the following departures from
Q135: Which of the following statements is false?<br>A)
Q151: A two-tailed test of hypothesis for a
Q192: A professor of mathematics refutes the claim