For a continuous random variable x, P(x  a) = P(x > a) and P(x
a) = P(x > a) and P(x 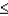 a) = P(x < a).
a) = P(x < a).
Definitions:
Warranty
A guarantee provided by a seller that a product will meet certain quality and performance standards over a specific time period.
Consumer Insurance
A financial product that provides coverage for individuals against potential losses related to their personal assets, health, or life.
Marginal Utility
The change in satisfaction or utility received by consuming an additional unit of a good or service.
Total Utility Function
A mathematical representation of the total satisfaction received from consuming a certain amount of goods or services.
Q14: A manufacturer of golf balls uses a
Q16: Suppose a 90% confidence interval for the
Q33: The National Rifle Association chapter in a
Q44: The set of all simple events of
Q50: Even though the normal probability distribution deals
Q62: A numerical descriptive measure calculated from the
Q114: The probability the 1993-94 flu vaccine immunizes
Q123: A machine produces aluminum tins used in
Q159: The standard error of the sampling distribution
Q162: An Internet server claimed that its users