Let x be a binomial random variable with n = 20 and p = 0.05.
Calculate 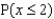 using the cumulative binomial probabilities table in Appendix I of your book.
using the cumulative binomial probabilities table in Appendix I of your book.
______________
Use the Poisson approximation to calculate 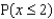 .
.
______________
Compare your results. Is the approximation accurate?
______________
Definitions:
Legal Right
An entitlement derived from a legal system that allows or empowers a person to act in a certain way or requires others to interact with the person according to specified rules.
Binding Contract
An agreement between parties that is legally enforceable in a court of law.
Promissory Estoppel
Promissory estoppel is a legal doctrine that can enforce a promise in the absence of a formal contract when a party has relied on that promise to their detriment.
Consideration
Something of value that is exchanged between parties in a contract, making the agreement legally binding.
Q12: From past experience, it is known 90%
Q20: Data integrity requires that data be complete,
Q56: An analytics manager, Lawrence, wants to clean
Q58: For any distribution, if the mean is
Q73: The scores on an aptitude test are
Q78: A recent survey of university faculty reported
Q85: Tchebysheff's Theorem states that the percentage of
Q91: If P(A) = 0, P(B) = 0.4,
Q94: A pie chart is a portrayal of
Q153: The population of Pepsi cans filled by