Byron's Manufacturing makes tables. Demand for the next four months and capacities of the plant are shown in the table below. Unit cost on regular time is $40. Overtime cost is 150% of regular time cost. Subcontracting is available in substantial quantity at $75 per unit. Holding costs are $5 per table per month; backorders cost the firm $10 per unit per month. Byron's management believes that the transportation algorithm can be used to optimize this scheduling problem. The firm has 50 units of beginning inventory and anticipates no ending inventory.
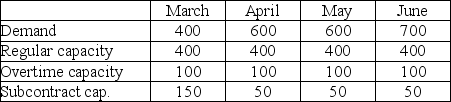 Answer the following questions based on the data table and solution table shown below.
Answer the following questions based on the data table and solution table shown below.
Byron's Manufacturing
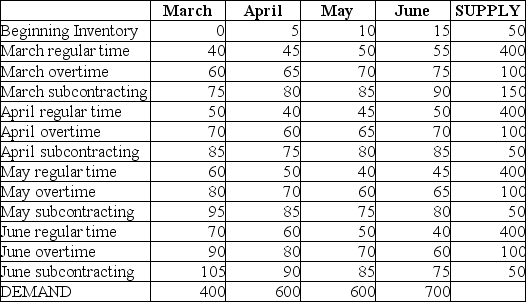 Byron's Manufacturing Solution
Byron's Manufacturing Solution
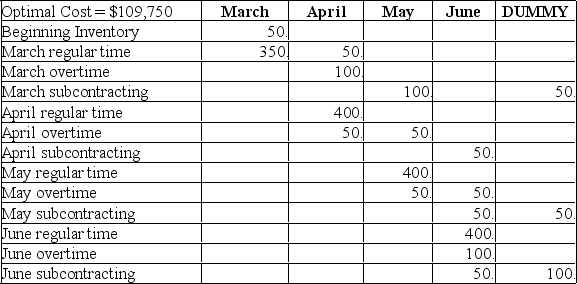 (a) How many units will be produced on regular time in June?
(a) How many units will be produced on regular time in June?
(b) How many units will be produced by subcontracting over the four-month period?
(c) What will be the inventory at the end of April?
(d) What will be total production from all sources in April?
(e) What will be the total cost of the optimum solution?
(f) Does the firm utilize the expensive options of subcontracting and backordering? When; why?
Definitions:
Extreme Scores
Data points in a dataset that are significantly higher or lower than the majority of the data, often considered outliers.
Sunk-Cost Fallacy
The misconception that ongoing investment in a project should continue based on the cumulative prior investment (sunk costs) regardless of the current and future costs and benefits.
Variety Seeking
The tendency of consumers to seek diversity and change in their choices or experiences.
Cybermediaries
Online intermediaries that facilitate transactions or information flow between businesses and consumers.
Q16: Consider the following product structure. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8322/.jpg"
Q31: A(n) _ is a list of quantities
Q42: In MRP, the number of units projected
Q43: A newspaper boy is trying to perfect
Q94: The factor weighting model is an attempt
Q101: Which of the following characteristics makes revenue
Q104: If a factory wants to cut its
Q111: There are two jobs to be assigned
Q119: Which of the following statements is TRUE
Q303: Job expansion can lead to increased labor