Figure: Profit Maximization in Monopolistic Competition 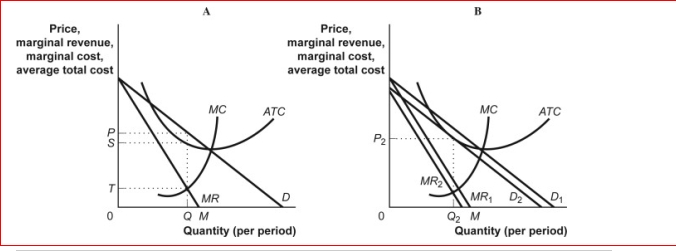
 (Figure: Profit Maximization in Monopolistic Competition) In panel B of the figure Profit Maximization in Monopolistic Competition, the long-run equilibrium will result in:
(Figure: Profit Maximization in Monopolistic Competition) In panel B of the figure Profit Maximization in Monopolistic Competition, the long-run equilibrium will result in:
Definitions:
Symptoms
Observable signs or experiences reported by a patient indicating the presence of a disease or medical condition.
Prescription Privilege
The legal authorization for certain professionals, typically healthcare providers like psychiatrists and psychologists in some jurisdictions, to prescribe medications.
Debate
A formal discussion on a particular topic in a public meeting or legislative assembly, in which opposing arguments are put forward.
Meta-Analyses
A research method that combines the results of multiple scientific studies to arrive at a comprehensive conclusion in a specific field of study.
Q42: In order to maximize profits, an airline
Q59: Figure: Market Failure <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1063/.jpg" alt="Figure: Market
Q61: Product differentiation under monopolistic competition means that
Q70: (Table: Demand Schedule for Gadgets) Look at
Q82: Your friend Angelina is the owner of
Q85: Price discrimination leads to a _ price
Q86: A monopolistically competitive firm has a downward-sloping
Q104: If monopolistically competitive firms are earning positive
Q153: On hot summer days, beach parking lots
Q182: A player's best action (regardless of the