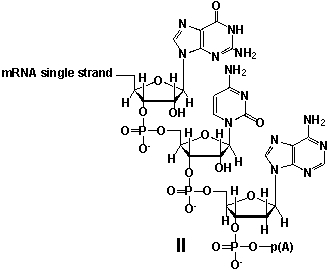
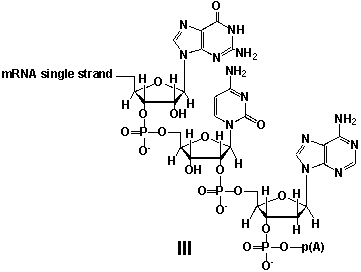
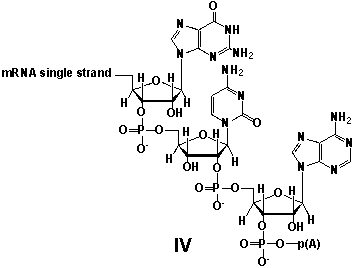
Whereas mRNA is basically "ready to use" after transcription in non-eukaryotes, eukaryotic mRNA requires extensive processing (see question 21) . In the process called polyadenylation a poly(A) tail is added to the 3'end of the mRNA strand (approx. 250 adenosine residues) . What is the chemical structure of the 3'-end of the mRNA strand after polyadenylation?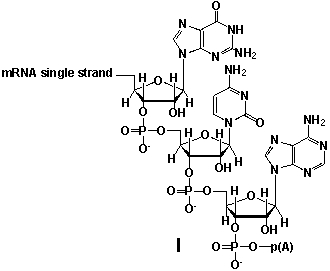
Definitions:
Rational Expectations School
An economic idea that assumes individuals make predictions about the future based on all available information and past experiences in a rational manner.
Monetary Policy
The process by which a central bank controls the supply of money in an economy, typically targeting inflation, employment, and economic growth.
Potential Level
The potential level of output, or potential GDP, is the maximum amount of goods and services an economy can produce when it is fully utilizing its resources, without causing inflation to rise.
Fixed-growth-rate Monetary Policy
A monetary policy framework aiming to maintain a predetermined rate of growth in the money supply.
Q1: If you become ill, how might your
Q4: Which is the major product from the
Q5: What are the staples of the Asian
Q8: Acetone reacts with 2 equivalents of molecular
Q31: The opacity of a crystalline polymer correlates
Q41: Tyrosine has an isoelectric point of 5.63.
Q45: The major product of the following reaction
Q103: Valuable traits in an employee DO include
Q115: In the basic communication model, when someone
Q117: A good meeting is a series of