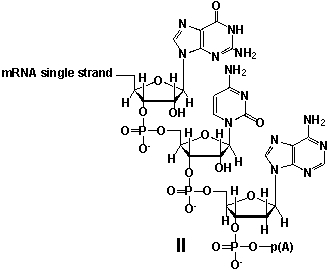
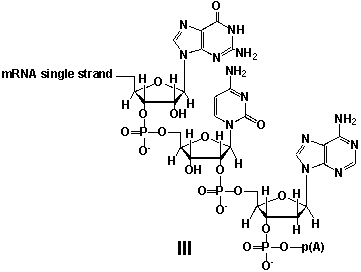
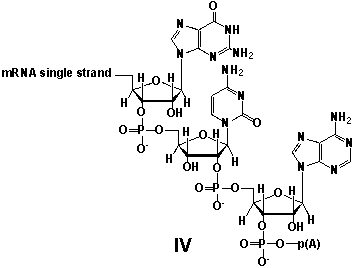
Whereas mRNA is basically "ready to use" after transcription in non-eukaryotes, eukaryotic mRNA requires extensive processing (see question 21) . In the process called polyadenylation a poly(A) tail is added to the 3'end of the mRNA strand (approx. 250 adenosine residues) . What is the chemical structure of the 3'-end of the mRNA strand after polyadenylation?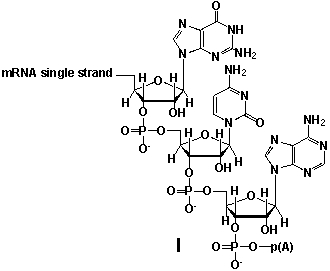
Definitions:
Owner's Equity
The portion of a company's total value that belongs to its owners or shareholders, calculated as the company's total assets minus its total liabilities.
Liabilities
Obligations or debts that a company owes to others, typically the sums of money due to creditors, suppliers, or tax departments.
Acquisition Value
The total cost incurred to acquire an asset, including the purchase price and all other expenses directly tied to the acquisition process.
Certified Public Accountant
A designation given to accounting professionals in numerous countries around the globe, indicating they have passed a licensure examination and met statutory and licensing requirements.
Q1: Which are the most important contributing structures
Q5: For African Americans, how might diet affect
Q20: What is the pH of a solution
Q24: An ether solution containing all of the
Q32: Which is a prostaglandin? <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8498/.jpg" alt="Which
Q34: Kapton is a polyimide developed by DuPont
Q45: What is the order of decreasing reactivity
Q62: Which of the following structures represents coenzyme
Q87: Which of the following is a tip
Q109: Which of the following is TRUE about