Maltose is a disaccharide formed from two units of D-Glucose. The production of maltose from germinating cereal grains (such as barley) is called malting, which is the first step of the brewing process. During germination, the concentration of amylases, which are the enzymes producing maltose from starch, is maximal. Maltose is then consumed by yeast, which produces ethanol and carbon dioxide. What type of glycosidic bond can you discern? 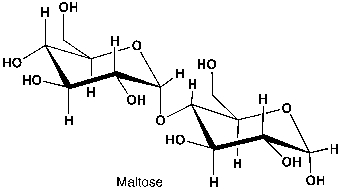
Definitions:
Dorsal and Ventral Roots
The two types of nerve roots; dorsal roots carry sensory information to the spinal cord, while ventral roots carry motor information from the spinal cord to the muscles.
Thymus Gland
A lymphoid organ situated in the neck of vertebrates that produces T-cells for the immune system.
Estrogen
A group of steroid hormones that promote the development and maintenance of female characteristics in the human body.
Pelvic Cavity
The body cavity located within the pelvis, housing organs such as the bladder, rectum, and for women, reproductive organs.
Q3: What health problems have become common for
Q20: Which of the labeled bonds is a
Q26: What is the reaction mechanism of the
Q33: How many principal vibrations does aspartame have?
Q38: Which is the number of stereocenters in
Q43: The first four amino acids of the
Q43: Which is the IUPAC name for the
Q45: The _ cm<sup>-1</sup> region is characteristic of
Q60: What are the main structural differences between
Q114: Communication becomes less important as you take