The enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of glutamic acids leads to gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA) , which is a common neurotransmitter in the human brain. What is the chemical structure of GABA? 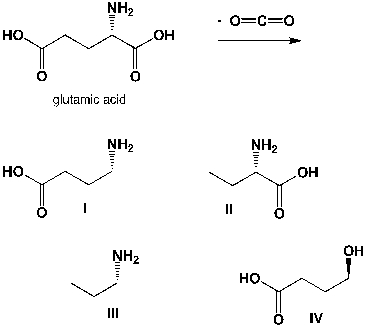
Definitions:
AIDS-Infected
A term used to describe individuals who have been infected by the HIV virus and have developed the advanced state of the infection, known as Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
SIDS
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, an unexplained death of a seemingly healthy baby, typically during sleep, in infants under one year old.
Sleep On Backs
A recommended sleeping position for infants to reduce the risk of Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS), also known as the supine sleeping position.
Breast Milk
The milk produced by a woman's breasts following childbirth, providing essential nutrients and antibodies to the infant.
Q6: Amylose and amylopectin are unbranched components of
Q9: A carbonate, which forms the backbone of
Q12: Which are the correct pairings of bases
Q15: Which compounds are acetals? <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8498/.jpg" alt="Which
Q20: The structure of the 3S,4R enantiomer of
Q23: DNA-supercoiling occurs because of the following phenomena:<br>I.
Q31: The opacity of a crystalline polymer correlates
Q39: The IUPAC name of the following compound
Q47: The IUPAC name of the following compound
Q52: Partial hydrolysis of phenobarbitol gives which compounds?