Below is a diagram representing a solvent A(l) in a 1-L beaker, and a solute X dissolved in the solvent. Solvent A has a density of 0.8 g/mL, and a molar mass of 40 g/mol. Solute X has a molar mass of 30 g/mol. Each circle of X represents 1 mol of X. Assume that the solute addition does not significantly change the volume of liquid in the beaker. 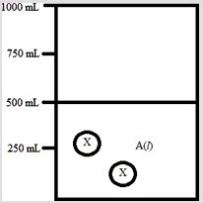 What is the molality of the solute X in this solution?
What is the molality of the solute X in this solution?
Definitions:
Stage Perspective
A viewpoint in developmental psychology that suggests individuals progress through a series of discrete stages of cognitive or emotional development.
Stage Theory of Development
A theory that proposes human development happens in distinct stages, each characterized by specific cognitive, social, or moral developments.
Predictable Order
A sequence of events or stages that occur in a consistent and known pattern, allowing for anticipation of what comes next.
Sensitive Periods
Critically defined periods in early development when the individual is especially receptive to certain stimuli and learning experiences.
Q8: List the components in an oxoacid.
Q21: A(n) _ liquid crystal is ordered in
Q32: A solution is prepared by adding 0.10
Q46: Since zirconium is a metal, ZrO<sub>2</sub> is
Q56: Which is a basic oxide?<br>A) NO<sub>2</sub><br>B) H<sub>2</sub>O<br>C)
Q68: Which of these polymers is used in
Q77: Sucrose decomposes to fructose and glucose in
Q80: Gases form heterogeneous mixtures or solutions with
Q109: Picric acid has been used in the
Q131: The solubility of nitrogen gas in water