TABLE 15-4
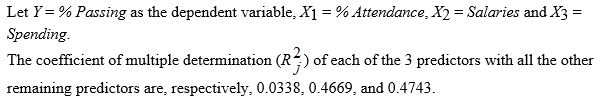
The output from the best-subset regressions is given below:
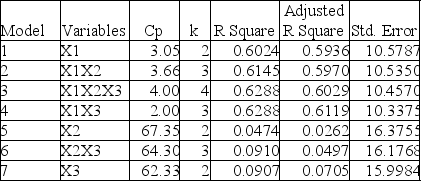
Following is the residual plot for % Attendance:
Following is the output of several multiple regression models:
Model (I):
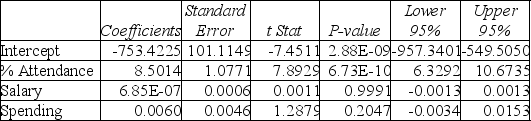
Model (II):
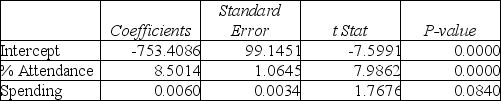
Model (III):
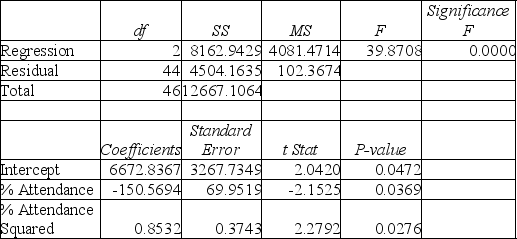
-Referring to Table 15-4, what is the p-value of the test statistic to determine whether the quadratic effect of daily average of the percentage of students attending class on percentage of students passing the proficiency test is significant at a 5% level of significance?
Definitions:
Economies of Scale
Refers to the cost advantages that enterprises obtain due to their scale of operation, with cost per unit of output decreasing with increasing scale.
Profit-Maximizing
A strategy or process where a firm determines the price, output level, or operational efficiency that will yield the highest possible profit.
Nondiscriminating Monopolist
A monopolist who charges the same price to all consumers for its products, regardless of differences in demand or willingness to pay.
Allocative Efficiency
Achieved when resources are distributed in a way that maximizes the net benefit to society, ensuring that each good is produced up to the point where the last unit provides a marginal benefit equal to the marginal cost of producing it.
Q29: Select the response that identifies or corresponds
Q29: Referring to Table 14-17 Model 1, we
Q70: Referring to Table 13-13, the p-value of
Q83: A regression diagnostic tool used to study
Q121: Referring to Table 14-18, what is the
Q142: Referring to Table 14-19, which of the
Q168: Referring to Table 16-14, to obtain a
Q228: Referring to 14-16, what is the correct
Q297: Referring to Table 14-10, the regression sum
Q336: Referring to Table 14-17 Model 1, there