The following image describes which type of change? 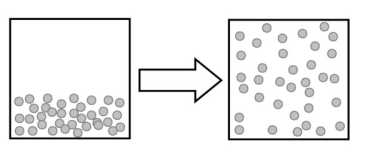
Definitions:
Production Rules
A hypothesized mental representation of procedural memory that specifies a goal to be achieved, one or more conditions that must be true in order for the rule to be applied, and one or more actions that result from the application of the rule.
Typicality Effect
The phenomenon whereby experimental participants are faster to respond to typical instances of a concept (e.g., robin for the concept “bird”) than to atypical instances (e.g., penguin for the concept “bird”).
Cognitive Economy
A principle of hierarchical semantic networks such that properties and facts about a node are stored at the highest level possible. For example, the fact “is alive” would be stored with the node for “animal” rather than stored with each node under animal such as “dog” and “cat.”
Encoding Specificity
A principle of retrieval asserted by Tulving. At the time material is first put into long-term memory, it is encoded in a particular way, depending on the context present at the time. At the time of recall, the person is at a great advantage if the same contextually supplied information available at encoding is once again available.
Q11: A proton and an electron are placed
Q21: A floating leaf oscillates up and down
Q29: If carbonic acid (H₂CO₃)were to undergo ionization,
Q29: The electrical force between charges is strongest
Q52: Since some of the compounds that are
Q58: The ionic bonds within cesium chloride, CsCl,
Q65: Resonance can be looked at as forced
Q81: If you eat metallic sodium or inhale
Q146: How many electrons are gained or lost
Q244: Why doesn't the sodium atom gain seven