Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Monopoly Profits in Duopoly 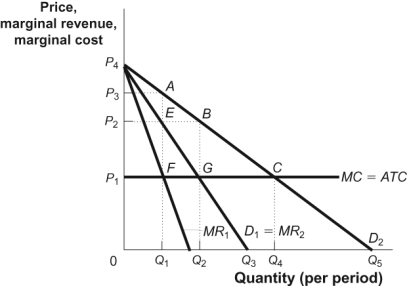
-(Figure: Monopoly Profits in Duopoly) The figure Monopoly Profits in Duopoly shows how an industry consisting of two firms that face identical demand curves (D1) can collude to increase profits. If the firms collude to share the market demand equally, then each firm will act as if its marginal revenue curve is given by:
Definitions:
Percent of Receivables Method
A method used in accounting to estimate bad debts expense based on a percentage of accounts receivable judged to be uncollectible.
Unadjusted Trial Balance
A financial report that shows the balances of all accounts, including assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses before any adjustments are made for the accounting period.
Bad Debts Expense
An expense reported on the income statement reflecting the cost of accounts receivable that a company does not expect to collect.
Factoring Fee Expense
A cost incurred by a business when it sells its accounts receivable to a third party (the factor) at a discount.
Q46: Suppose a perfectly competitive industry is suddenly
Q56: (Table: Coal Mine Pollution) The table Coal
Q92: (Table: Externalities from Parks) The table shows
Q107: (Figure: Monopoly Profits in Duopoly) Look at
Q115: (Table: Two Rival Gas Stations) Look at
Q128: (Figure: Monopolistic Competition IV) The firm in
Q156: If a monopolist is producing a quantity
Q215: Industries that are made up of many
Q258: A firm that is in an oligopoly
Q314: A firm that has economies of scale:<br>A)