Use the following to answer questions: 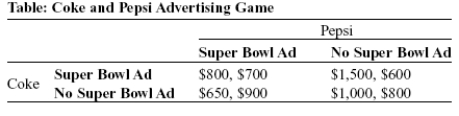
-(Table: Coke and Pepsi Advertising Game) Look at the table Coke and Pepsi Advertising Game. The soft-drink industry is dominated by Coca-Cola and Pepsi, and each firm spends a lot of money on advertising. Suppose each firm is considering a costly television commercial during halftime of the Super Bowl. The table shows the payoff matrix of profits that each firm would receive from their advertising decision, given the advertising decision of their rival. Profits in each cell of the payoff matrix are given as (Coke, Pepsi) . If both firms expect to play this game every year for the foreseeable future, in the outcome Coke _____ and Pepsi _____.
Definitions:
Average Cost
The total cost of production divided by the number of units produced, indicating the cost per unit.
Consumer Surplus
The bifurcation between what a consumer wishes to pay for a service or good, and what ends up being spent.
Producer Surplus
The difference between what producers are willing to sell a good for and the actual market price of the good.
Deadweight Loss
Deadweight loss refers to the loss of economic efficiency that can occur when the equilibrium for a good or a service is not achieved or is not achievable, often due to market distortion such as taxes or subsidies.
Q14: The largest Herfindahl-Hirschman index possible is _,
Q94: Suppose the price elasticity of demand for
Q99: (Figure: The Profit-Maximizing Output and Price) Look
Q100: An unwritten, unspoken agreement through which firms
Q105: (Figure: Computing Monopoly Profit) Look at the
Q129: The market for grade A large eggs
Q139: The effect of product differentiation is to
Q165: Which of the following is a form
Q207: General Snacks is a typical firm in
Q277: If there are many firms in an