In the oceans on either side of the Isthmus of Panama are 30 species of snapping shrimp; some are shallow-water species, others are adapted to deep water. There are 15 species on the Pacific side and 15 different species on the Atlantic side. The Isthmus of Panama started rising about 10 million years ago. The oceans were completely separated by the isthmus about 3 million years ago.
In the figure, the isthmus separates the Pacific Ocean on the left (side A) from the Atlantic Ocean on the right (side B) . The seawater on either side of the isthmus is separated into five depth habitats (1-5) , with 1 being the shallowest.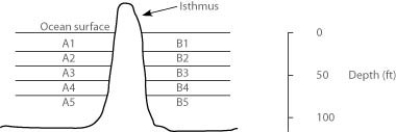
The Panama Canal was completed in 1914, and its depth is about 50 feet. After 1914, snapping shrimp species from which habitats should be most likely to form hybrids as the result of the canal?
Definitions:
Activity-Based Costing
A costing methodology that assigns expenses to products or services based on the activities that go into their production or delivery.
Machine-Hours
A unit of measure representing the operating time of a machine, used in cost accounting to allocate machine-related overheads to products.
Product Margin
The profit made on selling a product, calculated by deducting the total cost of production from the sales revenue of the product.
Activity-Based Costing
A costing method that assigns costs to products based on the activities they require.
Q3: Which of the following organisms is a
Q25: Which eukaryotic kingdom includes members that are
Q27: Members of two different species possess a
Q41: Which of the following processes occurs when
Q44: SAR is a group defined by DNA
Q44: Use the following figure and information to
Q45: Use the figure to answer the question.<br><img
Q47: Proto-oncogenes can change into oncogenes that cause
Q48: Given that phylogenies are based on
Q67: What is the function of the release