Use the following information to answer the question.
Canadian and Swiss researchers wanted to know if the diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) was important to the productivity of grasslands (M.G.A. van der Heijden, J. N. Klironomos, M. Ursic, P. Moutoglis, R. Streitwolf-Engel, T. Boler, A. Wiemken, and I. R. Sanders. 1998. Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability, and productivity. Nature 396:69-72) . Specifically, they wanted to know if it mattered which specific AMF species were present, or just that some type of AMF was present. They grew various plants in combination with one of four AMF species (A, B, C, and D) , no AMF species (O) , or all four AMF species together (A + B + C + D) ; and they measured plant growth under each set of conditions. All plant species were grown in each plot, so they always competed with each other with the only difference being which AMF species were present.
On the graphs, the x-axis labels indicate the number and identity of AMF species (bar 0 = no fungi; bars A - D = individual AMF species; bar A + B + C + D = all AMF species together) . The y-axis indicates the amount (grams) of plant biomass for the species shown in italics above each graph. Graph e is the total biomass (grams) of all 11 plant species combined; graph f is the biomass of Bromus erectus plants only, separated from the total.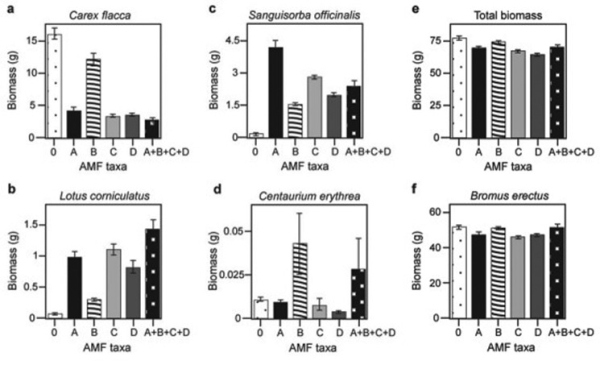
What is the most likely explanation for the observation that total biomass (graph e) does not vary with AMF diversity?
Definitions:
Founder Effect
A genetic phenomenon that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals, leading to a reduction in genetic variation.
Genetic Flow
The transfer of genetic material between populations of the same species or between different species, leading to changes in genetic makeup.
Genetic Drift
A mechanism of evolution involving random fluctuations in the frequency of alleles within a population, which can cause genetic variation to decrease over time.
Bottleneck
A sudden decrease in a population size caused by adverse environmental factors; may result in genetic drift; also called genetic bottleneck or population bottleneck.
Q19: Arrange the following structures from largest to
Q23: Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic that targets prokaryotic
Q24: You are the lucky student of a
Q26: The earliest known mineralized structures in vertebrates
Q35: The presence of a lophophore in a
Q43: The advantages of the reduced gametophytes in
Q60: In a bacterium that possesses antibiotic resistance
Q66: With which of the following statements would
Q67: Which one of the following statements about
Q75: Which of the following characteristics evolved independently