Use the following figure and information to answer the question.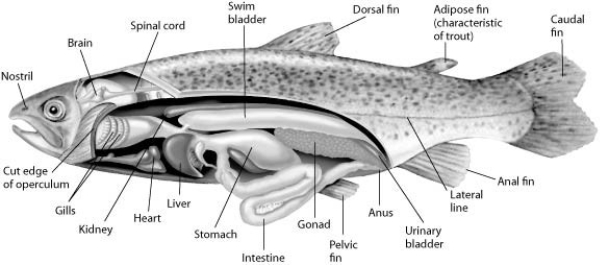
Fishes that have swim bladders can regulate their density and, thus, their buoyancy. There are two types of swim bladder: physostomous and physoclistous. The ancestral version is the physostomous version, in which the swim bladder is connected to the esophagus via a short tube (see the figure) . The fish fills this version by swimming to the surface, taking gulps of air, and directing them into the swim bladder. Air is removed from this version by "belching." The physoclistous version is more derived and has lost its connection to the esophagus. Instead, gas enters and leaves the swim bladder via special circulatory mechanisms within the wall of the swim bladder.
If a ray-finned fish is to both hover (remain stationary) in the water column and ventilate its gills effectively, then what other structure besides its swim bladder will it use?
Definitions:
Confidence Interval
A range of values derived from sample statistics that is likely to contain the true value of an unknown population parameter.
Null Hypothesis
In statistics, a hypothesis that proposes no significant difference or effect; the hypothesis that a researcher tries to disprove.
Alpha Level
The threshold of significance in hypothesis testing, representing the probability of making a Type I error.
Confidence Interval
A range of values, derived from sample statistics, used to estimate the true parameter of a population with a specified level of confidence.
Q1: Which of the following can function in
Q16: A typical angiosperm embryo sac (female gametophyte)has
Q20: One important difference between the anatomy of
Q23: The metabolic rate of an animal is
Q26: Use the following information to answer the
Q31: Foods can be preserved in many ways
Q52: What major benefits do plants and mycorrhizal
Q57: Which of the following statements about the
Q57: Use the figure to answer the following
Q63: Most land-dwelling invertebrates and all of the