Suppose the formula for wind chill C (in degrees Fahrenheit) is given by 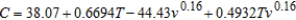 where v is the wind speed in miles per hour and T is the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. The wind speed is
where v is the wind speed in miles per hour and T is the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. The wind speed is 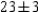 miles per hour and the temperature is
miles per hour and the temperature is  Fahrenheit. Use
Fahrenheit. Use 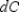 to estimate the relative error in calculating the wind chill. Round your answer to two decimal places.
to estimate the relative error in calculating the wind chill. Round your answer to two decimal places.
Definitions:
Sequential
Describes a process that follows a specific order or sequence, where each step or stage comes one after the other in a logical progression.
Transitivity
The cognitive ability to recognize logical relationships among elements in a serial order and to deduce the third relation from the first two.
Formal Operations
The fourth and final stage of Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development, characterized by the ability to think abstractly, reason logically, and manage hypothetical situations.
Cognitive Development
The process by which a child learns to reason, solve problems, and understand concepts throughout different stages of early life.
Q20: Find the moments of inertia for a
Q34: Given <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8527/.jpg" alt="Given and
Q53: Use the properties of the derivative to
Q57: Find the x-values (if any) at which
Q76: Find the eccentricity and distance from the
Q83: Find the vertices of the ellipse given
Q108: An open box of maximum volume is
Q122: Consider the region <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8527/.jpg" alt="Consider the
Q139: Find an equation of the tangent line
Q168: For <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8527/.jpg" alt="For ,