Exhibit: Short-Run Phillips Curve 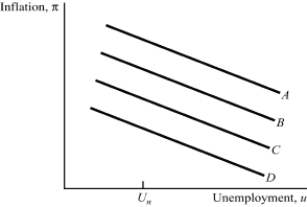 As the short-run Phillips curve shifts from A to B to C to D:
As the short-run Phillips curve shifts from A to B to C to D:
Definitions:
Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum in the brain, involved in high-level brain functions such as thought, emotion, reason, and language.
Brainstem
The portion of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord, playing a key role in regulating vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Broca Area
A region of the frontal lobe in the brain associated with language processing, speech production, and comprehension.
Distorted Speech
A modification of speech sounds that renders them unclear or unintelligible, often resulting from neurological disorders, hearing impairment, or environmental factors.
Q5: Holding output, Y, fixed, a reduction in
Q10: The debt-deflation hypothesis explains the fall in
Q10: A supply shock does not occur when:<br>A)a
Q11: In a small open economy with a
Q11: Other things being equal, all of the
Q30: The life-cycle model assumes that consumers use
Q49: Explain how the Solow growth model differs
Q51: Starting from long-run equilibrium in the dynamic
Q60: In the Solow growth model, the steady-state
Q82: How would an adverse supply shock change