A firm has a production function given by 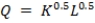
. Suppose that each unit of capital costs R and each unit of labor costs W.
a. Derive the long-run demands for capital and labor.
b. Derive the total cost curve for this firm.
c. Derive the long-run average and marginal cost curves.
d. How do marginal and average costs change with increases in output? Explain.
e. Confirm that the value of the Lagrange multiplier you get from the cost minimization problem is equal to the marginal cost curve.
Definitions:
Infinite Size
A concept often used in population genetics to describe a population so large that genetic drift and sampling errors are negligible.
Landscape Genetics
An interdisciplinary field that combines landscape ecology and population genetics to understand how geographical and environmental features affect gene flow and genetic variation.
Spatial Statistics
A subfield of statistics that deals with analyzing spatially referenced data, taking into account the topological, geometric, and geographic properties that might affect the observed measurements.
Landscape Ecology
A discipline that studies the spatial patterns, processes, and effects of landscapes, encompassing the interactions between spatial patterns and ecological processes.
Q2: (Figure: Cost and Quantity of Output II)
Q58: Suppose that U = min{2X, Y}, where
Q59: In a perfectly competitive industry, the long-run
Q69: In the market for used cars, the
Q85: Suppose that the perfectly competitive market for
Q103: (Figure: Average Total Cost and Quantity of
Q116: (Table: Total and Marginal Revenue II) Use
Q119: Allen earns $1,000 per week and purchases
Q120: Answer the following questions.<br>a. Marcie is enrolled
Q127: A firm spends $12,000 per day producing