(Figure: Budget Constraint for Work or Leisure I) 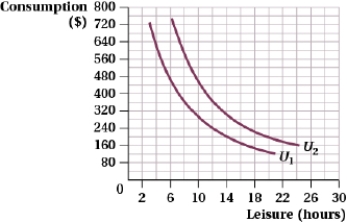
a. Graph a budget constraint assuming a person has 24 hours that can be used for work or leisure at a wage rate of $20. Note the optimal consumption-leisure bundle.
b. Graph a budget constraint assuming a person has 24 hours that can be used for work or leisure at a wage rate of $30. Note the optimal consumption-leisure bundle.
c. Determine both the income and substitution effects on the graph.
Definitions:
Gross Profit
The difference between sales and the cost of goods sold.
Periodic Inventory Method
An accounting approach where inventory is physically counted at specific intervals to determine the cost of goods sold and ending inventory levels.
Beginning Inventories
Beginning inventories are the value of a company's inventory at the start of an accounting period, serving as a basis for determining the cost of goods sold.
Ending Inventories
The final value of goods available for sale at the end of an accounting period, calculated through physical count or estimation.
Q20: The costs of obtaining a college degree
Q25: (Figure: Budget Constraint I) If Katarina earns
Q41: Suppose a firm has two types of
Q59: Consumers value high-quality dirt bikes at $6,000
Q70: Daiyu's parents have decided to save for
Q70: (Table: Insurance Claims) Five people vary in
Q87: Suppose the demand faced by a labor
Q100: There are no externalities in the market
Q124: (Figure: Type A and Type B I)
Q164: (Table: Maximum Willingness to Pay IV) Suppose