Suppose two sweaters compete in a Bertrand market structure with differentiated products. Demand for the first sweater is given by 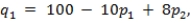 where p1 is price for sweater 1 and p2 is the price for sweater 2. Demand for the second sweater is
where p1 is price for sweater 1 and p2 is the price for sweater 2. Demand for the second sweater is 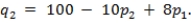
The costs of providing the sweaters are C1 = q1 and C2 = q2 respectively. The first sweater firm will charge $____ for its sweater.
Definitions:
Manufacturing Factory Overhead
All indirect costs associated with the manufacturing process, excluding direct materials and direct labor expenses.
Production Department
Definition: A specific division within a company focused on the process of producing goods and services.
Factory Overhead Rate
A measure used to allocate the total factory overhead costs to units produced, based on a predetermined activity base.
Plantwide Factory Overhead Rate
The plantwide factory overhead rate is a single rate used to allocate all of a plant's manufacturing overhead costs to its production activities, based on a common basis such as direct labor hours.
Q3: Your economics professor decides to cancel one
Q3: What are the three types of learners,
Q5: In the market for capital, the discovery
Q6: Choose any case containing data from text
Q15: A sand and gravel company sells pea
Q17: A union faces a labor demand curve
Q76: A market is served by two firms
Q103: The inverse demand for shampoo is given
Q133: To solve for a mixed-strategy equilibrium in
Q134: The market inverse demand curve for thrust