Suppose two colas compete in a Bertrand market structure with differentiated products. Demand for the first cola is given by 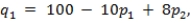
where p1 is price for cola 1 and p2 is the price for cola 2. Demand for the second cola is 
The costs of providing the colas are C1 = q1 and C2 = q2, respectively.
a. Identify firm 1's profit function.
b. Identify firm 2's profit function.
c. Identify firm 1's reaction function.
d. Identify firm 2's reaction function.
e. Identify the equilibrium price charged for each cola.
Definitions:
Primary Reinforcer
A primary reinforcer is a stimulus that satisfies basic survival needs without prior learning; examples include food, water, and shelter.
Conditioned Reinforcer
A stimulus that gains its reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer; also known as a secondary reinforcer.
Instinctive
Related to or denoting behavior that is innate and automatic, not learned from experience.
Human Behavior
The range of actions and mannerisms exhibited by humans in conjunction with their environment, influenced by culture, attitudes, emotions, values, ethics, authority, rapport, hypnosis, persuasion, coercion, and/or genetics.
Q1: A Competitive Coup in the In-Flight Magazine.
Q2: Under what kind of conditions would you
Q4: You receive the results of a paired-comparison
Q41: Jerome operates a car repair shop and
Q64: Suppose the payoffs for players A and
Q108: Answer the following questions.<br>a. Miserly Mark claims
Q148: Suppose that a night club's customers all
Q156: (Table: Firms A and B X) Two
Q156: (Figure: Type A and Type B I)
Q161: The price elasticity of demand for coffee