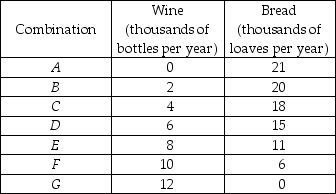
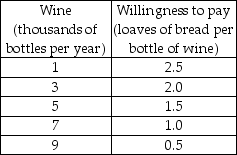
-The Hobbits of the Shire are trying to decide how much bread and how much wine to produce. They ask you to be their economic consultant and give you the information in the first table above about different combinations of wine and bread that they can produce if they are fully employed and doing their best. The Hobbits also give you the information in the second table above about their willingness to pay for wine depending on how much wine they already have. To help the Hobbits solve their problem:
a) Draw the Shire's production possibilities frontier. Put wine on the horizontal axis.
b) What is the opportunity cost of the first two thousand bottles of wine? What is the marginal cost of the 3000th bottle of wine? What is the marginal cost of the 3,000th loaf of bread?
c) Draw the marginal cost of wine curve. What happens to the marginal cost if production of wine increases? Why?
d) Draw the marginal benefit from wine curve on the same figure on which you put the marginal cost curve. Describe the relationship between the quantity of wine produced and the marginal benefit from wine.
e) What combination of bread and wine will you recommend the Hobbits to produce? Why? Explain to the Hobbits why they would be worse off by producing a different combination of bread and wine.
Definitions:
Multiple Intelligences
A theory proposed by Howard Gardner, suggesting that individuals have different kinds of intelligences, including linguistic, logical-mathematical, musical, bodily-kinesthetic, spatial, interpersonal, and intrapersonal.
Behaviorism
A theory of learning that focuses on observable behaviors and suggests that all behaviors are acquired through conditioning processes without considering thoughts or feelings.
Behavioral Objectives
These are specific, measurable goals that describe the desired behavior outcomes of learning or intervention.
Didactic Lectures
A teaching method that involves the straightforward transmission of information from an instructor to a student, typical in traditional educational settings.
Q20: Increasing opportunity cost occurs along a production
Q36: In an eight-hour day, Andy can produce
Q46: As a person consumes more of a
Q94: When the opportunity cost of producing more
Q98: Using the table provided above, what can
Q121: In an ad for insurance, the text
Q178: Jane produces only corn and cloth. Taking
Q205: Pamela Michelle Scott, a low income single
Q314: Education<br>A) does not really add to one's
Q347: The table shows income distributions in the