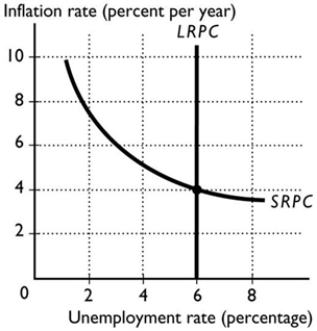
-Comparing the short-run Phillips curve and the long-run Phillips curve, we see that there is
Definitions:
Fixed-Cost Fallacy
Consideration of costs that do not vary with the consequences of your decision (also known as the sunk-cost fallacy).
Depreciation Costs
The allocation of the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life, representing the decline in value due to wear and tear, age, or obsolescence.
Opportunity Cost
The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when making a decision or choosing to pursue a particular action.
Accounting Costs
Costs that appear on the financial statements of a company.
Q7: The structural surplus<br>A) equals the actual surplus
Q26: If you buy a DVD player produced
Q31: When the quantity of real GDP demanded
Q45: When the Reserve Bank increases the cash
Q56: Suppose over the next few years the
Q58: An increase in the Australian interest rate
Q60: In the long run, a 3 per
Q80: A bank's desired reserve ratio is<br>A) the
Q86: In the aggregate expenditure (AE) model, the
Q105: A country produces only apples and bananas.