Figure 39.4
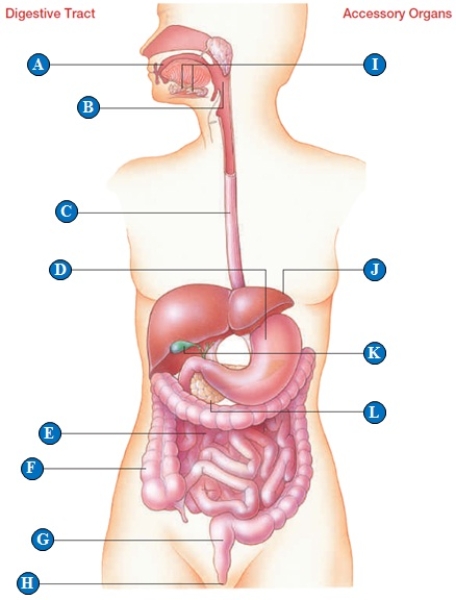
-salivary glands
Definitions:
Bedridden
Unable to leave bed due to illness, injury, or disability.
Community Health Nursing
A branch of nursing focused on the health care of individuals, families, and groups in a community, aiming to improve overall health and prevent diseases.
School Nursing
A specialized practice of nursing that advocates for the health and well-being of students within the school setting.
Community-Oriented Nursing
A branch of nursing focused on improving the health and well-being of the community by offering preventive and primary care services.
Q14: Which term refers to the structure and
Q19: Humans require 13 known vitamins in their
Q23: Which of the following elements is NOT
Q57: Which plant organs are often connected to
Q60: Which of the following hormones affects cells
Q60: empties into a collecting duct<br>A)ascending segment of
Q68: Which term refers to an extended period
Q78: What is the usual pH of stomach
Q85: degrading cell walls of pathogens<br>A)jasmonates<br>B)salicylic acid<br>C)phytoalexins<br>D)"antifreeze proteins"<br>E)oligosaccharins<br>F)PR
Q92: Which cells produce pepsinogen in the stomach?<br>A)