One model for the spread of an epidemic is that the rate of spread is jointly proportional to the number of infected people and the number of uninfected people. In an isolated town of 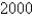 inhabitants,
inhabitants, 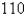 people have a disease at the beginning of the week and
people have a disease at the beginning of the week and 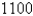 have it at the end of the week. How long does it take for
have it at the end of the week. How long does it take for 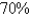 of the population to be infected?
of the population to be infected?
Definitions:
Fixed Costs
Costs that do not change with the level of goods or services produced within a certain range; such costs are incurred regardless of business activity levels.
Break-even Point
The point at which total income matches total costs, leading to a situation where there is no gain or deficit.
Variable Cost
Costs that vary directly with the level of production or the volume of services rendered, such as raw materials and direct labor.
Fixed Costs
Costs that remain constant regardless of the amount of products or services a company generates, including expenses like lease payments, wages, and premiums.
Q2: Determine whether the series is absolutely convergent,
Q2: Solar radiation drives the distribution of weather
Q10: Gravel is being dumped from a conveyor
Q16: Find the limit <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8390/.jpg" alt="Find the
Q17: Label the structures in the following diagrams
Q33: Find the value of the expression accurate
Q33: By reading values from the given graph
Q39: Which food is an example of a
Q43: Calculate the iterated integral. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8390/.jpg" alt="Calculate
Q64: Find the area of the surface obtained