Radio stations often have more than one broadcasting tower because federal guidelines do not usually permit a radio station to broadcast its signal in all directions with equal power. Since radio waves can travel over long distances, it is important to control their directional patterns so that radio stations do not interfere with one another. Suppose that a radio station has two broadcasting towers located along a north-south line, as shown in the figure. If the radio station is broadcasting at a wavelength 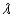 and the distance between the two radio towers is equal to
and the distance between the two radio towers is equal to 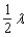 , then the intensity I of the signal in the direction
, then the intensity I of the signal in the direction 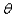 is given by
is given by 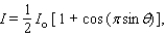 where I o is the maximum intensity.
where I o is the maximum intensity. 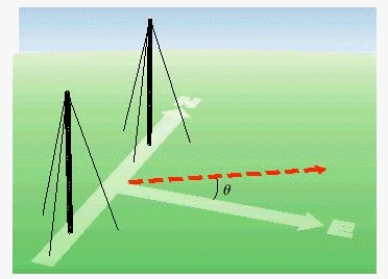 Approximate I in terms of I o for
Approximate I in terms of I o for 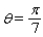 .
.
Definitions:
Project Profiling
A method used to analyze and assess various aspects of a project to understand its scope, complexity, and requirements.
System Scope
The defined boundaries and extent of a system, including its functionalities, objectives, and the users it serves.
Project Profile
An overview or summary of the essential aspects and characteristics of a project, including its scope, objectives, and status.
Project Attributes
Characteristics or features that define and distinguish a project, such as its scope, duration, and resources required.
Q17: Verify the identity. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg" alt="Verify the
Q21: The volume V of the right triangular
Q45: Approximate the acute angle <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg" alt="Approximate
Q50: Represent the complex number geometrically. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg"
Q59: Tell whether the reduction formula is correct
Q85: Find the fourth-degree polynomial function whose graph
Q99: Sketch the graph of the equation. <img
Q128: Use common logarithms to solve for x
Q135: If <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg" alt="If and
Q141: Given A (4, -3) and B (-12,