The phases of the moon can be described using the phase angle  , determined by the sun, the moon, and the Earth, as shown in the figure. Because the moon orbits Earth,
, determined by the sun, the moon, and the Earth, as shown in the figure. Because the moon orbits Earth,  changes during the course of a month. The area of the region A of the moon, which appears illuminated to an observer on Earth, is given by
changes during the course of a month. The area of the region A of the moon, which appears illuminated to an observer on Earth, is given by 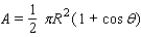 , where R = 1,080 mi is the radius of the moon. Approximate A for the following position of the moon:
, where R = 1,080 mi is the radius of the moon. Approximate A for the following position of the moon: 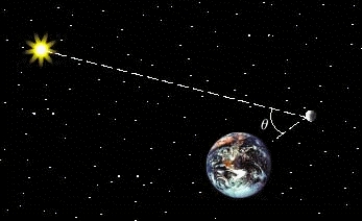
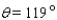
Definitions:
Break Even
The juncture where the aggregate of all costs matches the total income, leading to neither a profit nor a loss.
Short Run
A period of time during which at least one of a firm's inputs is fixed.
Long Run
A period in which all factors of production and costs are variable, allowing firms to adjust all inputs and achieve optimal operation.
Monopolistically Competitive
A market structure where many companies sell products that are similar but not identical, allowing for significant competition.
Q8: Sketch the graphs of the lines on
Q23: Let P ( t ) be the
Q33: Three solutions contain a certain acid. The
Q43: Find the exact values of the six
Q61: Find all values of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg" alt="Find
Q67: Find the solution of the equation. <img
Q122: Given that <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg" alt="Given that
Q127: Approximate, to the nearest 0.01 radian, all
Q129: Sketch the graph of the equation. <img
Q144: A forester, 210 feet from the base