Scientists sometimes use the formula 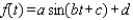 to simulate temperature variations during the day, with time t in hours, temperature f ( t ) in
to simulate temperature variations during the day, with time t in hours, temperature f ( t ) in  , and t=0 corresponding to midnight. Assume that f ( t ) is decreasing at midnight. Determine values of a, b, c, and d that fit the information: the high temperature is 17
, and t=0 corresponding to midnight. Assume that f ( t ) is decreasing at midnight. Determine values of a, b, c, and d that fit the information: the high temperature is 17  , and the low temperature of -17
, and the low temperature of -17  occurs at 4 A.M.
occurs at 4 A.M.
Definitions:
Memory Consolidation Theory
The Memory Consolidation Theory postulates that stable, long-term memories are formed from the transfer and reorganization of short-term memories during specific brain states.
Wish-Fulfillment Theory
A psychological concept proposed by Sigmund Freud suggesting that dreams represent the fulfillment of unconscious desires or wishes.
Information-Processing Theory
An approach to understanding how the human mind transforms sensory information, viewing the brain as a complex processing system that encodes, stores, and retrieves information.
Neural Activation Theory
A hypothesis explaining how neural circuits in the brain are activated to form memories or responses; often used in discussions of learning and memory. [Note: This is a conceptual rephrasing. The term "Neural Activation Theory" might not directly refer to a well-established theory by this precise name, but the description fits general understanding of how neural activation underpins cognitive functions.]
Q8: Write the expression as one logarithm. 9ln
Q36: Express the statement as a formula that
Q59: Tell whether the reduction formula is correct
Q64: Use matrices to solve the system. <img
Q78: If forces F<sub> 1 </sub>, F<sub> </sub><sub>2
Q84: Applying the first theorem on bounds for
Q95: If <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg" alt="If and
Q98: Find the partial fraction decomposition. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg"
Q142: Find an exponential function of the form
Q143: The volume V of the right triangular