The phases of the moon can be described using the phase angle  , determined by the sun, the moon, and the Earth, as shown in the figure. Because the moon orbits Earth,
, determined by the sun, the moon, and the Earth, as shown in the figure. Because the moon orbits Earth,  changes during the course of a month. The area of the region A of the moon, which appears illuminated to an observer on Earth, is given by
changes during the course of a month. The area of the region A of the moon, which appears illuminated to an observer on Earth, is given by 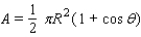 , where R = 1,080 mi is the radius of the moon. Approximate A for the following position of the moon:
, where R = 1,080 mi is the radius of the moon. Approximate A for the following position of the moon: 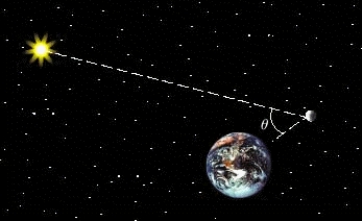
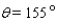
Definitions:
Q38: If c represents a constant force, find
Q53: Find all values of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg" alt="Find
Q60: Find the equation of the circle that
Q79: Find an equation using the cotangent function
Q94: Find all solutions of the equation. <img
Q96: Determine whether the given pair of vectors
Q99: In fishery science, a cohort is the
Q117: Sketch the graph of the function. <img
Q140: Verify the identity. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg" alt="Verify the
Q140: Solve the system <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB8634/.jpg" alt="Solve the