Figure 6.3 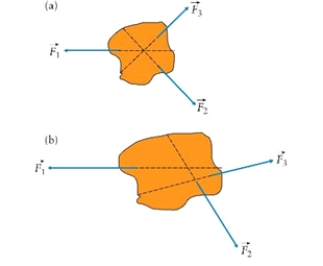 Concurrent forces and non-concurrent forces. (a) The lines of action of concurrent forces pass through a common point. (b) The lines of action of non-concurrent forces do not intersect at a common point.
Concurrent forces and non-concurrent forces. (a) The lines of action of concurrent forces pass through a common point. (b) The lines of action of non-concurrent forces do not intersect at a common point.
-Three forces are acting on objects as shown in Fig. 6.3. The vector sum of the forces is zero. Explain if there is any difference between the two cases: (a) the lines of action of concurrent forces pass through a common point, and (b) the lines of action of non-concurrent forces do not intersect at a common point. Are any of the two objects moving? Why or why not? If there were motion, what kind of motion would it be?
Definitions:
Voluntary Exchange
An economic transaction where all parties involved agree to the trade, believing they will benefit from the exchange.
Relative Scarcity
The economic concept referring to the limited availability of resources in comparison to the unlimited wants and needs of consumers.
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a good or service demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers, creating a market balance.
Equilibrium Quantity
The supply of goods or services equals the demand for them at the price where the market is in equilibrium.
Q9: Low-quality exchange subordinates get more _ when
Q14: Which of the following is a suggested
Q17: A gas is heated at a constant
Q23: A weight is swung on the end
Q27: A certain gas in a closed container
Q32: Can gravity act as a restoring force?
Q38: A uniform bar with a pivot (fulcrum)
Q41: The standard man from Fig. 4.10 intends
Q43: A student in an elevator is checking
Q48: A hockey player swings his stick to