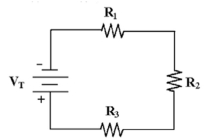
-Calculate VR2 and VR3 in Figure 4-1 if VR1=16V, R1=10 , R2=10 and R3=15
Definitions:
Research Hypothesis
Another term for alternative hypothesis, indicating the expected outcome or belief regarding a study's findings.
Null Hypothesis
In statistical testing, it posits there is no effect or no difference, serving as the default or hypothesis to be tested.
Alternative Hypothesis
A hypothesis that contradicts the null hypothesis, suggesting there is a significant difference or relationship between variables.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement in hypothesis testing that suggests no effect or no difference, serving as the default assumption to be tested against.
Q2: The quantity usually measured using a spring-supported
Q9: If I=45 mA and
Q20: Refer to Figure 20-2 (b). If
Q24: A basic instrumentation amplifier has three op-amps.
Q25: How much voltage is dropped across
Q30: The <i>Rotary</i> switch in Figure 2-1 is
Q62: No problems could occur if a 10
Q65: Which switch in Figure 2-1 could be
Q205: Differential amplifiers provide high voltage gain and
Q269: A forward biased silicon diode is in