SCENARIO: PAYOFF MATRIX FOR AIRBUS AND BOEING
The payoff matrix supplied shows outcomes of various strategies
That Airbus and Boeing might follow in response to action on the
Part of the other company.This payoff matrix describes actions
In developing socalled superjumbo jets that can carry 600 or
More passengers.In each element, the lowerleft value gives
The outcome for Boeing based on the action of Airbus and the
Upperright value gives the outcome for Airbus based on the
Action of Boeing.For example, in element A, each company will
Lose $10 million if they both decide to produce superjumbo jets. 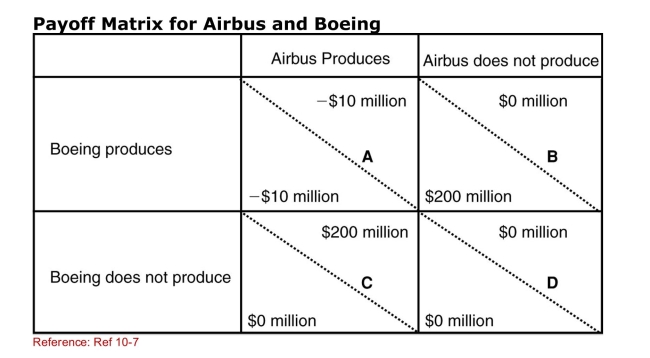
(Scenario: Payoff Matrix for Airbus and Boeing) Boeing has
Decided not to produce superjumbo jets.Instead, it will
Continue to market its 450passenger 747s.However, Airbus will
Produce superjumbo jets.Which element represents their joint
Decisions?
Definitions:
Net Operating Income
The total operating profit of a company after all operating expenses, excluding taxes and interest expenses, have been deducted from total revenue.
First Year
Refers to the initial period or the first 12 months of a specific timeframe, often used in the context of financial or operational performance.
Absorption Costing
A method of product costing that includes all manufacturing costs, both fixed and variable, in the cost of a product.
Contribution Margin
The amount remaining after variable costs have been subtracted from revenue, which contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit.
Q27: NAFTA is:<br>A)a free trade area among Mexico,
Q35: Which of the following is included in
Q53: A large nation's export subsidy _ importing<br>Countries'
Q58: The story about the mass slaughter of
Q61: Assume that two countries (Home and Foreign)
Q85: When products from a highcost country within
Q92: In the United States, which of the
Q92: The United States is a significant exporter
Q107: In a prisoner's dilemma:<br>A)all competing parties gain.<br>B)one
Q118: Many regional trade agreements include other provisions