TABLE 13-15
The superintendent of a school district wanted to predict the percentage of students passing a sixth-grade proficiency test. She obtained the data on percentage of students passing the proficiency test (% Passing), daily mean of the percentage of students attending class (% Attendance), mean teacher salary in dollars (Salaries), and instructional spending per pupil in dollars (Spending) of 47 schools in the state.
Following is the multiple regression output with Y = % Passing as the dependent variable, 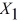 = : % Attendance,
= : % Attendance, 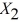 = Salaries and
= Salaries and 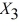 = Spending:
= Spending:
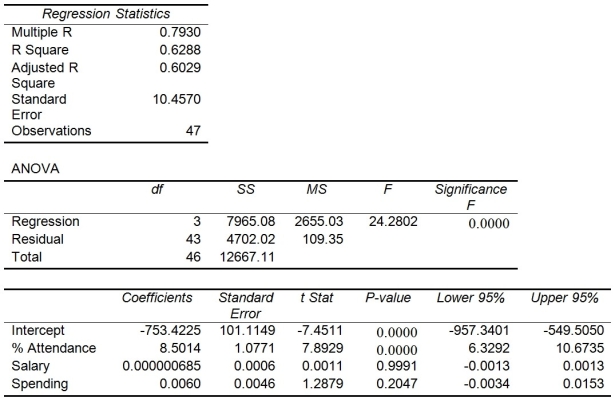
-Referring to Table 13-15, the null hypothesis should be rejected at a 5% level of significance when testing whether there is a significant relationship between percentage of students passing the proficiency test and the entire set of explanatory variables.
Definitions:
P-value
A measure in statistics that helps in determining the significance of results obtained in an experiment or survey. It indicates the probability of observing results as extreme as those observed if the null hypothesis is true.
Average Sales
The mean amount of sales over a certain period, calculated by summing all sales figures and dividing by the number of sales transactions.
Critical Value
A point on the scale of the test statistic beyond which we reject the null hypothesis; it marks the threshold for significance in hypothesis testing.
P-value
The odds of receiving outcomes in a test that are equally or more extreme than those observed, given the null hypothesis is assumed to be accurate.
Q1: Referring to Table 11-6, what is the
Q26: Referring to Table 11-10, for the cell
Q26: Developing operational definitions for each critical-to-quality characteristic
Q37: This concept describes a company's success when
Q75: Referring to Table 13-4, one individual in
Q77: Referring to Table 13-6, what is the
Q176: Referring to Table 12-13, the critical value
Q194: When an additional explanatory variable is introduced
Q201: Referring to Table 13-17 Model 1, the
Q224: Referring to Table 13-10, the multiple regression