Find the particular solution of the differential equation for the oscillating motion of an object on the end of a spring. In the equation, is the displacement from equilibrium (positive direction is downward) measured in feet, and is the time in seconds (see figure) . The constant is the weight of the object, is the acceleration due to gravity, is the magnitude of the resistance to the motion, is the spring constant from Hooke's Law, is the acceleration imposed on the system, and 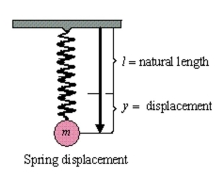
Definitions:
Methyl Isobutyrate
An organic compound with the formula C5H10O2, used as a flavoring agent and solvent.
Acid Chloride
Organic compounds belonging to the acyl chloride group, characterized by a carbon-oxygen double bond connected to a chlorine atom, used as intermediates in organic synthesis.
2° Amine
A type of amine where the nitrogen atom is attached to two alkyl or aryl groups and one hydrogen atom.
Compound
A compound is a substance formed when two or more chemical elements are chemically bonded together.
Q14: Break‑even analysis does not indicate the output
Q21: Trade credit is primarily used by retailers
Q45: What is the annual rate of interest
Q52: If the internal rate of return of
Q53: Find an equation in rectangular coordinates
Q57: The radius of a right circular
Q59: <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\text { Use Stokes's Theorem
Q91: Use a change of variables to
Q100: Find the directional derivative of the
Q115: Find the limit. <span class="ql-formula"